Have you ever wondered what is in your vape juice? With the recent concerns about vaping-related illnesses, it’s natural to question the safety of e-cigarettes. One rumor that has been circulating is that vapes contain urine. But is there any truth to this claim?
The answer is no, vapes do not contain urine. This rumor likely started because some studies have found traces of a chemical called acetamide in e-cigarette vapor. Acetamide is a breakdown product of urea, which is found in urine, but it’s also found in many other sources such as tobacco smoke, coffee, and bread. The amount of acetamide found in e-cigarette vapor is very small and is not a cause for concern.
What are Vapes?
Vapes, also known as electronic cigarettes or e-cigarettes, are battery-powered devices that heat a liquid (e-juice or vape juice) to create an aerosol (vapor) that is inhaled. The liquid typically contains nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals.
Vapes come in various shapes and sizes, but most consist of a battery, a heating element, and a tank or cartridge that holds the liquid. Some vapes are disposable, while others are refillable and can be used multiple times.
Vaping has become increasingly popular, especially among young people, as an alternative to smoking cigarettes. However, vaping is not without risks, and there is still much that is not known about the long-term effects of vaping.
Some of the potential risks associated with vaping include:
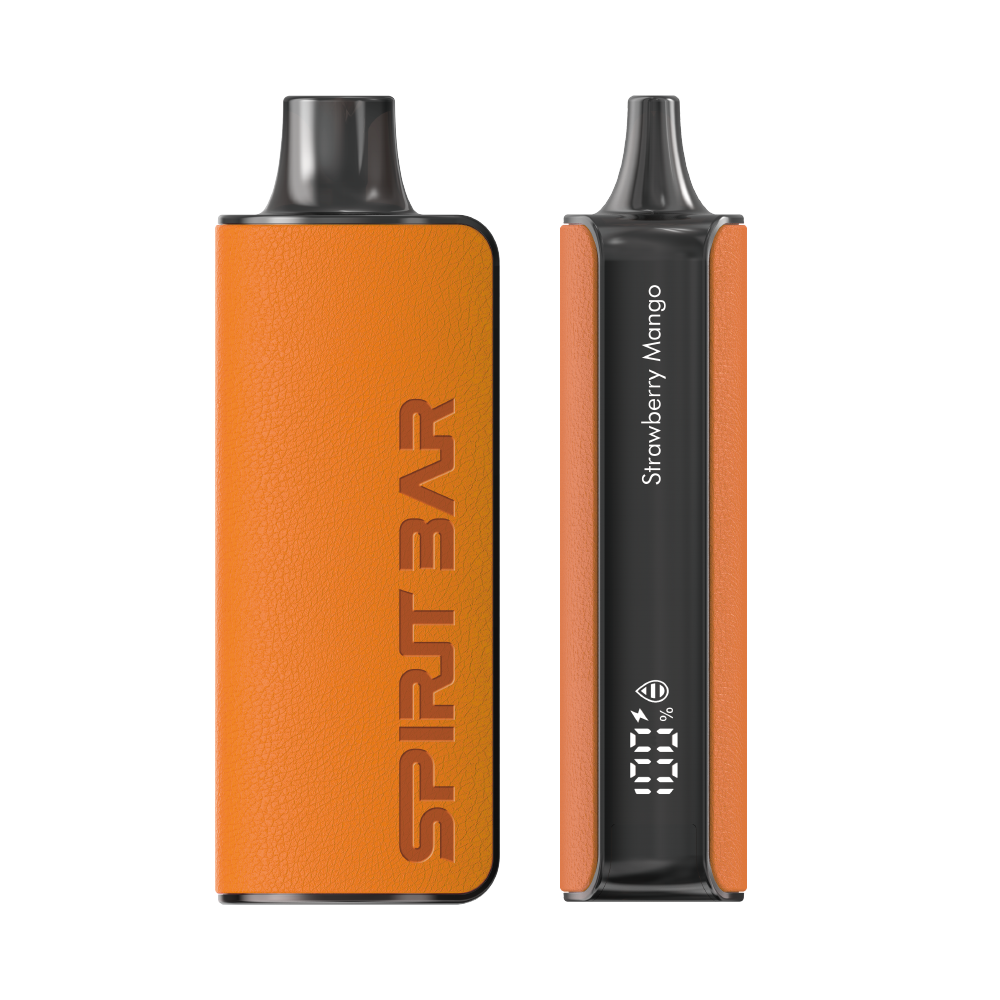
SPIRITBAR Katana BP10000
- Slender, leather-textured body reminiscent of a katana handle for an authentic samurai feel
- Unique samurai-inspired e-liquid flavor - fruity yet not too sweet, with a luxurious, elegant aroma
- Powerful 650mAh rechargeable battery for extended vaping time
- Large 18ml e-liquid capacity and 10,000 puff capacity
- Advanced mesh coil and e-liquid & power display screens for optimal vaping experience
The special juice captures the essence of the samurai spirit with its rich, smoothly pulsating flavor that brings new satisfaction with every puff. The device's slender, leather-textured design evokes the grip of a samurai's katana, making this product a perfect choice for beginner vapors.
- Addiction to nicotine
- Lung damage and respiratory problems
- Cardiovascular problems
- Exposure to harmful chemicals and metals
It is essential to understand the risks associated with vaping before deciding to use these devices. If you are considering vaping as an alternative to smoking, it is recommended that you speak with a healthcare professional to discuss the potential risks and benefits.
Common Misconceptions about Vapes
There are many misconceptions about vapes and vaping that have been circulating for years. Here are a few of the most common myths about vapes:
Urine in Vapes Myth
One of the most persistent myths about vapes is that they contain urine. This is completely false. There is absolutely no evidence to suggest that vapes contain urine, and the idea is simply absurd.
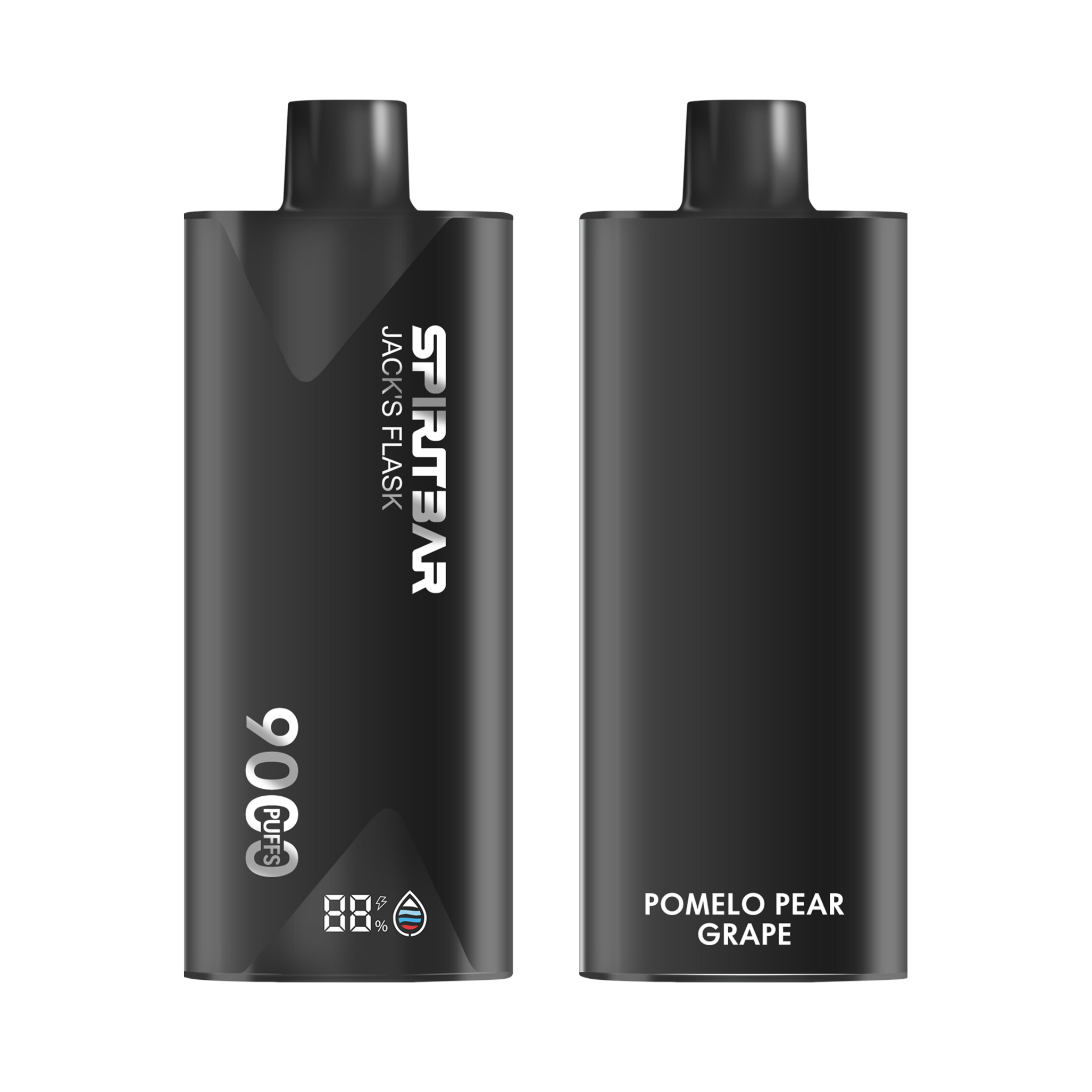
SPIRITBAR Jack’s Flask 9000 Puffs
- Stylish pirate flask-shaped body providing an exciting vaping experience
- Delivering up to 9000 puffs per device
- 20ml e-liquid capacity with 50mg nicotine strength for satisfying throat hit
- Specialized pirate-themed e-juice flavors for rich, swirling taste
- Premium mesh coil optimizes flavor profile for maximum vaping enjoyment
This disposable vape captures the daring spirit of the high seas with its flask styling and signature pirate e-juice flavors. The extraordinary battery life provides 9000 indulgent puffs for extended vaping pleasure. Live boldly and freely with the Jack's Flask - a legendary vaping experience fit for a pirate's adventures.
The myth seems to have originated from a viral video that claimed to show a person extracting urine from a vape cartridge. However, the video was quickly debunked as a hoax. The person in the video was actually using a syringe to extract e-liquid from a cartridge, not urine.
Despite the lack of evidence, the urine in vapes myth continues to circulate on social media and other online platforms. It’s important to remember that just because something is being shared widely online doesn’t mean it’s true.
If you’re concerned about the safety of vapes, there are plenty of legitimate concerns to consider. For example, while vaping is generally considered to be less harmful than smoking, it’s still not completely risk-free. Nicotine vaping is not risk-free, but it is substantially less harmful than smoking [1]. Additionally, there have been cases of e-cigarette or vaping use-associated lung injury (EVALI) and deaths attributed to that condition [2].
It’s always a good idea to do your own research and consider the facts before making any decisions about your health. Don’t believe everything you read online, and be sure to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about vaping or any other health-related issues.
Composition of Vape Juice
When it comes to vaping, the composition of the vape juice is an important factor to consider. Vape juice, also known as e-liquid, is the liquid that is heated in an electronic cigarette to create an aerosol that is inhaled by the user. The ingredients in vape juice can vary based on the brand and flavor, but generally, they contain the following components:
Ingredients of Vape Juice
- Propylene glycol (PG): This is a clear, odorless liquid that is commonly used as a food additive. It is used in vape juice to help distribute the flavor evenly and create a smooth throat hit. PG is generally recognized as safe by the FDA when used in small quantities.
- Vegetable glycerin (VG): This is a thick, sweet liquid that is derived from vegetable oils. It is used in vape juice to create thick clouds of vapor and add sweetness to the flavor. VG is also generally recognized as safe by the FDA when used in small quantities.
- Flavorings: Vape juice can contain a wide variety of flavorings, ranging from fruity to dessert flavors. These flavorings are usually made from natural or artificial ingredients and are added to the PG/VG base to create a unique flavor profile.
- Nicotine: This is an optional ingredient in vape juice and is used to satisfy nicotine cravings. Nicotine is an addictive substance and can have negative health effects, so it is important to use it responsibly.
- Solvents: Solvents are used to dissolve the nicotine and flavorings in the PG/VG base. Common solvents include ethyl alcohol, distilled water, and acetone.
It is important to note that while these ingredients are generally recognized as safe by the FDA, there is still a lot of debate surrounding the safety of vaping. Some studies have suggested that vaping can have negative health effects, while others have found it to be a safer alternative to smoking traditional cigarettes. Ultimately, it is up to you to decide whether or not vaping is right for you.
Health Concerns of Vaping
Vaping has become a popular alternative to smoking in recent years, but it is not without its health concerns. Here are some of the short-term and long-term effects of vaping.
Short-Term Effects
Nicotine Addiction
Like smoking, vaping can lead to nicotine addiction. Nicotine is a highly addictive substance that can cause cravings and withdrawal symptoms if you try to quit. According to Mayo Clinic, studies have shown that it may be harder to quit a nicotine addiction than a heroin addiction.
SPIRITBAR Katana BP10000
- Slender, leather-textured body reminiscent of a katana handle for an authentic samurai feel
- Unique samurai-inspired e-liquid flavor - fruity yet not too sweet, with a luxurious, elegant aroma
- Powerful 650mAh rechargeable battery for extended vaping time
- Large 18ml e-liquid capacity and 10,000 puff capacity
- Advanced mesh coil and e-liquid & power display screens for optimal vaping experience
The special juice captures the essence of the samurai spirit with its rich, smoothly pulsating flavor that brings new satisfaction with every puff. The device's slender, leather-textured design evokes the grip of a samurai's katana, making this product a perfect choice for beginner vapors.
Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
Vaping can also cause your heart rate and blood pressure to increase. This is because nicotine raises your blood pressure and spikes your adrenaline. This can increase your heart rate and the likelihood of having a heart attack.
Respiratory Problems
Vaping can cause respiratory problems, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. This is because vaping can cause irritation and inflammation in your lungs.
Long-Term Effects
Lung Damage
Vaping can cause long-term lung damage, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer. According to a study by New York University, e-cigarette smoke can lead to DNA harm in the lining of the bladder.
Increased Risk of Heart Disease
Vaping can also increase your risk of heart disease. According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, vaping can cause your arteries to narrow, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Other Health Risks
Vaping is still a relatively new phenomenon, so there may be other health risks associated with it that we don’t yet know about. However, some studies have suggested that vaping can weaken your immune system and increase your risk of respiratory infections.
In conclusion, while vaping may be less harmful than smoking, it still poses health risks that you should be aware of. If you’re considering vaping, it’s important to weigh the potential risks against the benefits.
Regulations on Vape Juice Ingredients
When it comes to vape juice ingredients, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has set regulations that manufacturers must follow. The FDA requires manufacturers to list all ingredients on the packaging, including any additives or flavors. They also prohibit certain ingredients that are harmful to human health.
Some of the prohibited ingredients include diacetyl, which has been linked to a serious lung disease called bronchiolitis obliterans, and vitamin E acetate, which has been linked to lung injuries. Additionally, the FDA has set limits on the amount of nicotine that can be included in vape juice.
Manufacturers must also adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) to ensure the safety and consistency of their products. This includes using clean facilities, properly storing ingredients, and testing the final product for quality and safety.
It’s important to note that while the FDA regulates vape juice ingredients, they do not test every product on the market. It’s still possible for harmful ingredients to be present in some products, particularly those purchased from unregulated sources.
Overall, it’s important to be aware of the ingredients in your vape juice and to purchase products from reputable manufacturers that follow FDA regulations.
Public Perception and Misinformation
The public perception of vaping has been heavily influenced by misinformation and myths. One such myth is that vapes contain urine. This rumor has been circulating on social media and other platforms, leading to confusion and concern among vapers and non-vapers alike.
Despite the lack of evidence to support this claim, it continues to be shared widely. This misinformation can be harmful as it may deter people from using vapes and lead to misconceptions about the safety of vaping.
It is important to note that vapes do not contain urine or any other bodily fluids. Vapes typically contain a combination of propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, flavorings, and nicotine (in some cases). These ingredients are carefully selected and tested to ensure that they are safe for consumption.
Misinformation about vaping can erode the credibility of public health officials and organizations. A study found that individuals who trust e-cigarette companies more than public health officials are more likely to believe that vaping is safer than smoking [[1]].
To combat misinformation about vaping, it is important to rely on credible sources of information and to fact-check claims before sharing them. Public health officials and organizations can also play a role in dispelling myths and educating the public about the risks and benefits of vaping.
In conclusion, the claim that vapes contain urine is a myth that has been perpetuated by misinformation. It is important to rely on credible sources of information and to fact-check claims before sharing them.